CFATS - Risk Management for Chemicals of Interest
/What is CFATS: Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards?
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) uses a risk-based tiering methodology that incorporates aspects of vulnerability, consequence and threat in determining if a facility possessing certain chemicals is considered high risk. The Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards (CFATS) program focuses on identifying and regulating these facilities to ensure security measures are in place that reduce the risk of misuse of their chemicals.
Chemicals of Interest (COI)
Such chemicals, known as chemicals of interest (COI), if released, stolen, used as a contaminant, sabotaged or weaponized have the potential to create a significant negative impact to human life and/or health. There are over 300 COI along with their screening threshold quantities (STQ), concentrations and security issues specified in Appendix A of the CFATS regulations. COI are designated based on hazards associated with toxicity, flammability and explosiveness. Other factors also include facility location and vulnerability along with the potential for lives lost during a significant incident.
CFATS Covered Chemical Facilities
Affected industries may include but are not limited to chemical plants, chemical storage facilities, electrical generating facilities, refineries, universities (laboratories) and manufacturing.
How does the CFATS process work?
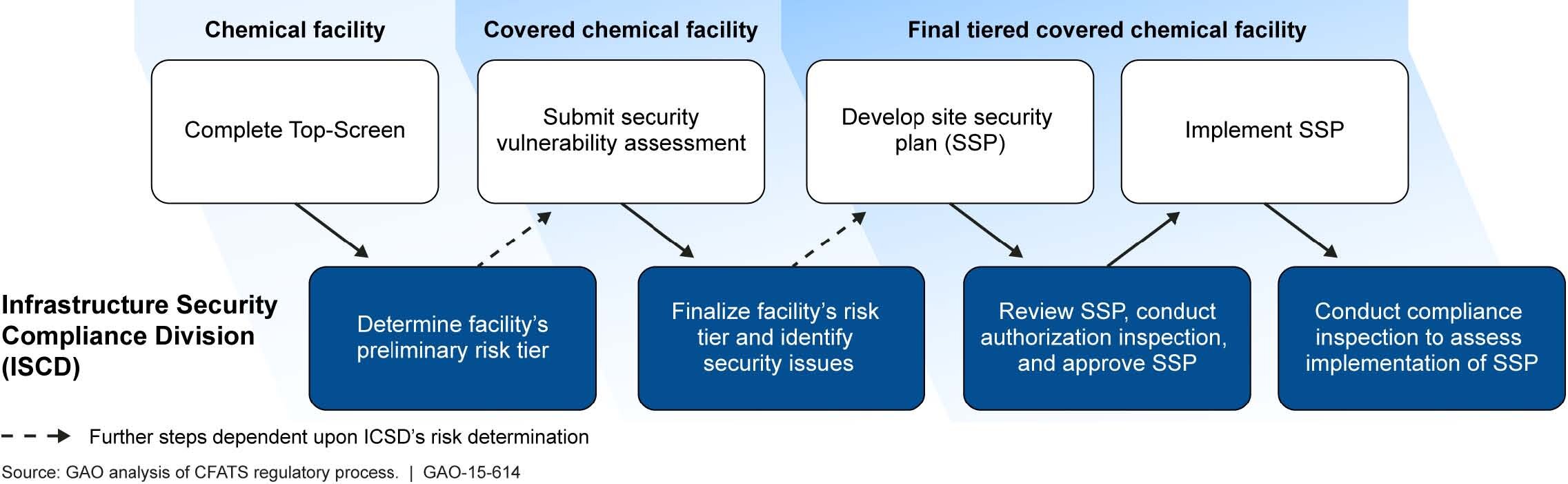
Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards (CFATS) Process
CFATS Compliance Steps
Any facility that meets or exceeds the screening threshold quantities (STQ) for any COI would be considered a “chemical facility” and must report possession to the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) by proceeding with the following steps:
Register for a Chemical Security Assessment Tool (CSAT) account at https://csat-regulation.dhs.gov/.
Complete a Top-Screen which is an easy-to-use online survey that is used to report chemical holdings and facility information to the DHS.
The DHS will then assess the overall risk of the affected facility based on the information that was provided.
As a result of the assessment, one of four tiers with Tier 1 representing the highest risk, may be assigned to that facility.
There may also be a determination made at this time that there is not a high risk associated.
If a Tier level is assigned, then a facility must provide a security vulnerability assessment via the CSAT identifying the use of COI, critical assets, and measures related to the facility’s policies, procedures, and resources that are necessary to support the site’s security plan. This assessment also provides an analysis of the existing security measures and any potential vulnerabilities.
Complete either a site security plan or alternative security program that meets criteria in the risk-based performance standards according to the assigned tier level and unique circumstances which are involved.
A site security plan must be submitted via the CSAT and meet the risk-based performance standards.
An alternative security program may be submitted in the place of a site security plan. With this option, a facility develops its own template for addressing requirements such as describing the facility’s security measures and how they meet or exceed applicable risk-based performance standards.
Tier 3 and 4 facilities also have the option to submit an Expedited Approval Program (EAP) SSP in lieu of an SSP or ASP.
What to include in your Site Security Plan
CFATS Risk-Based Performance Standards (RBPS)
It is recommended that covered facilities develop “written” policies and procedures addressing the Risk-Based Performance Standards (RBPS) as applicable to the Tier level of the affected facility. By documenting these planned measures within a Site Security Plan, alternative security plan, or other type of plan, implementation is simplified and compliance easily maintained.
The Risk-Based Performance Standards include:
Securement of Perimeter
Securement of critical assets
Screening and access control to the facility and restricted areas
Determent, detection and delay of a potential attack.
Shipping, receipt and storage of hazardous materials
Theft deterrence and diversion of potentially dangerous chemicals
Sabotage deterrence
Cyberattack deterrence
Emergency response
Monitoring, communications and warning systems
Personnel training
Personnel surety
Protective measures for elevated threats
Specify threats, vulnerabilities and/or risks
Defining what kinds of security incidents (physical and cyber) are “significant” and should be reported up the internal chain of command, to the DHS, other Federal agencies, state or local law enforcement and first responders.
Identifying, responding to, investigating, and reporting all significant security incidents as well as suspicious activities.
Officials and organizations for security and compliance
Maintenance of records
Failure to report chemicals of interest to the Department of Homeland Security and knowingly submitting false information can result in a violation. Failure to implement an effective site security plan and to maintain records can result in an infraction as well. Don’t take a chance! Check your chemicals today and report them as required.
KERAMIDA is a full-service security, environmental, health and safety consulting firm that has a Chemical-Terrorism Vulnerability Information (CVI) Authorized User who can assist with guidance on the CFATS process. Services offered include performing site assessments and providing written plans applicable to the security measures of the affected facility. Call (800) 508-8034 or contact us today to speak with one of our security professionals on how we can assist you with CFATS compliance.
Contact
Daniel Engling, MS, CIH, CSP
Vice President, Safety and Industrial Health Services
KERAMIDA Inc.
Contact Dan at dengling@keramida.com.